Fatty liver disease
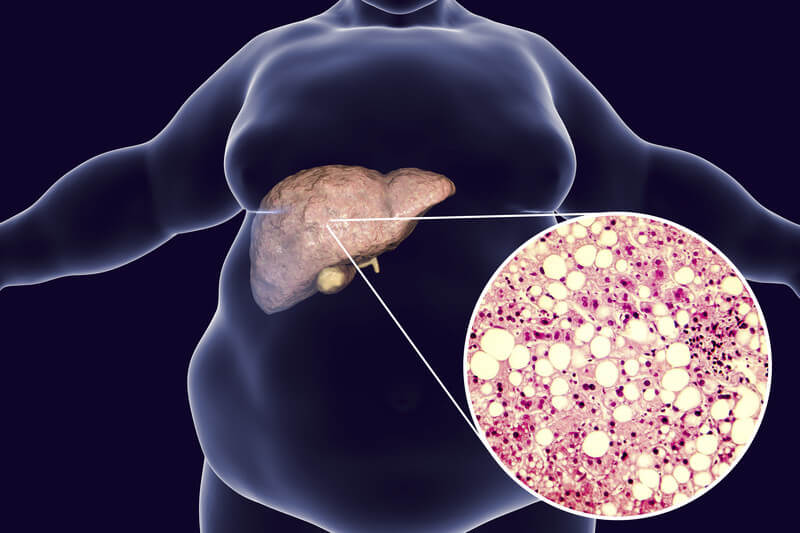
Fatty liver disease
What is fatty liver disease:
Hepatic steatosis, which is also known as Fatty liver disease, essentially means that there is a lot of fat in your liver. At all times, there is a bit of fat stored in your liver for it to use as energy. However, high levels of fat in your liver can lead to serious health issues such as liver failure, diabetes, kidney disease and much more.
Symptoms of fatty liver:
If you suspect that you may have fatty liver disease, especially when it starts becoming too negatively impactful on your day-to-day life, we strongly recommend that get it checked up. These are a few common symptoms:
– Severe weakness or tiredness
– Jaundice (yellow eyes and skin)
– Loss of appetite
– Pain in your upper right abdomen (where the liver is located)
– Weight loss
Risk factors of getting fatty liver:
Fatty liver disease can happen to anyone, but certain risk factors greatly increase the likelihood of having it, such as:
– Certain medication
– Elderly age
– High fat diet
– Obesity
– Type 2 diabetes
– Genetics
– Excessive alcohol consumption
Types of fatty liver:
Alcohol-related fatty liver disease (ALD):
o Almost all heavy drinkers develop fatty liver disease since alcohol encourages the build up of fat in the liver. ALD gets alleviated by abstaining from alcohol, but continued drinking leads to serious issues. For example, an enlarged liver, which causes discomfort or pain in the area around your liver. There’s also alcoholic hepatitis, which causes your liver to get inflamed and leads to problems like jaundice, pain, nausea and fever.
o If the drinking and fatty liver disease continues, then Alcoholic cirrhosis occurs. Cirrhosis is when there’s a buildup of scar tissue in your liver, which is your liver’s response to the inflammation.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):
o Even if a person doesn’t drink alcohol excessively/at all, they are still able to get fatty liver disease. In which case, it is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and there are 2 types.
Simple fatty liver means that there is fat in your liver, but it’s not causing detrimental issues like inflammation or damage to your liver. It usually doesn’t get worst and many people with simple fatty liver live normal lives unaffected by it.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) means that the fat in your liver causes inflammation and damage, which is very serious and can lead to cirrhosis (build up of scar tissue which impairs liver functions and can cause liver failure or liver cancer).
Why it’s important to be checked:
Your liver plays a crucial role in your metabolism (creating energy for the body from nutrients, food and drinks). For example, it produces bile that helps enzymes digest fat; stores and release glycogen (a substance that can be broken down and release energy); and filters out or breaks down toxic substances like alcohol and medication into less toxic and more digestible substances.
Excess fat in your liver, however, can cause impaired function in these vital processes and, more seriously, liver failure. If your fatty liver disease becomes too severe (e.g getting cirrhosis), the only option to treat it may be to replace your liver completely/partially with a liver transplant. Cirrhosis is irreversible but fortunately, cirrhosis only happens at the end (hence why it’s sometimes called late-stage liver disease) so there’s opportunity to prevent it from getting to that state.
What can be done:
Fortunately, fatty liver disease has a high chance to be reversed or alleviated if treated early. Unfortunately, there is no set standard nor medication for fatty liver disease. Most doctors will recommend a few things though:
Quit drinking or drink in moderation
– Alcohol only makes the damage much worst, so talking with your doctor about detox programs to help with alcohol abstinence is recommended.
Lose weight
– Fatty liver disease is caused by excess fat, so losing body weight will reduce the amount of fat in your body. This includes managing your diet to have less cholesterol and fats, along with regular exercise.
How fatty liver disease is checked:
A simple one is a physical examination, where the doctor will weigh you and then palpate for the liver, meaning they feel the area around the liver for irregularities like tenderness. There’s also a liver biopsy, where a small sample of your liver is removed and sent to the lab for examination. Similarly, a blood test can be done to check the level of liver enzymes present in your blood, which are indicators of fatty liver disease.
Despite those, imaging is the recommended way of checking for fatty liver as it is quite accurate and not invasive. An ultrasound can be used to get an image of the liver for the doctors to determine whether you have or don’t have fatty liver disease. The same imaging can be used for other things related to the liver like it’s size, shape or presence of abnormalities like cancers.