 vs
vs 
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
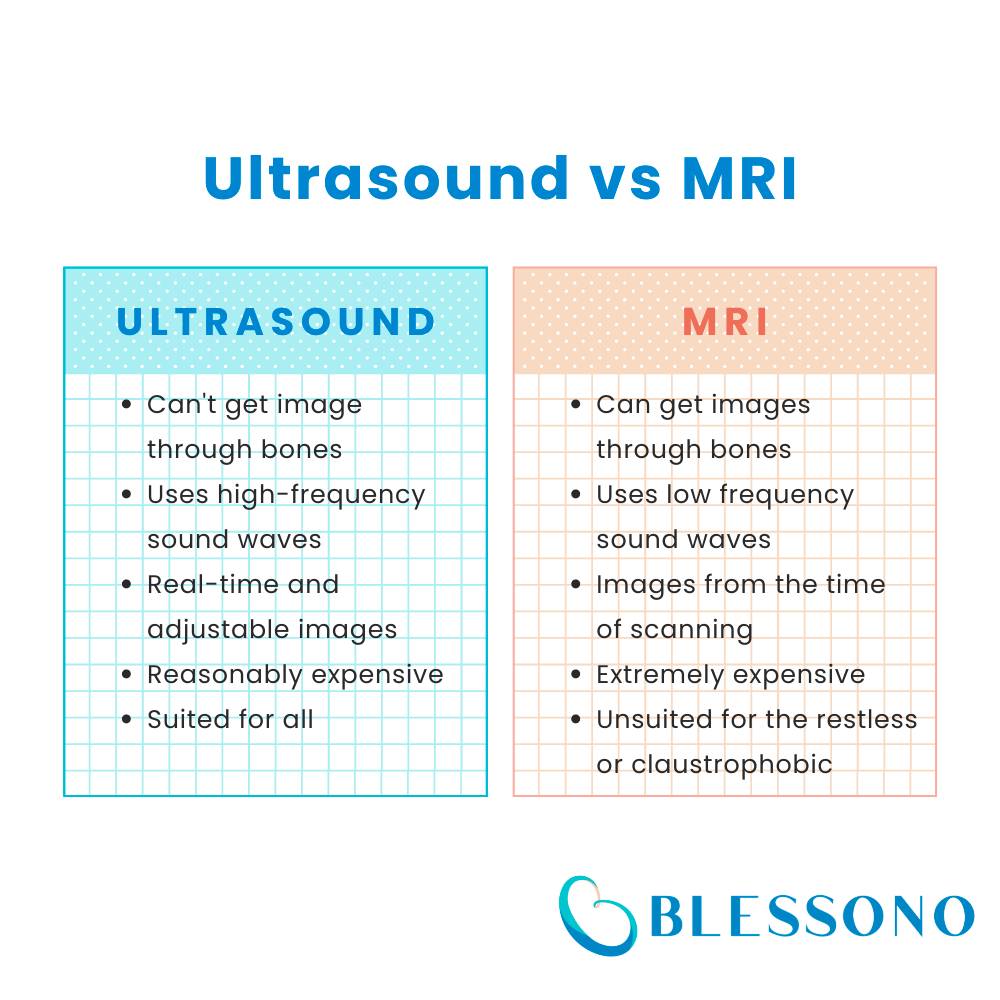
- Purpose: MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging modality that utilizes a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and computer processing to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. It is particularly useful for imaging soft tissues, such as the brain, muscles, and organs.
- Advantages:
- MRI does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for repeated scans.
- The high-resolution images produced by MRI can be used to visualize small structures, such as blood vessels, in great detail.
Ultrasound:
- Purpose: Ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging modality that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs and tissues. It is used primarily to visualize soft tissues and organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, and uterus, and is also used to visualize fetuses during pregnancy.
- Advantages:
- Ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a relatively low-risk option compared to other imaging modalities.
- The real-time capabilities of ultrasound allow physicians to observe the movement of organs and blood flow.
- Ultrasound is portable and can be performed quickly, making it a convenient option for bedside examinations or emergency situations.
In summary, both MRI and Ultrasound are valuable diagnostic tools in the field of medicine. The choice of which modality to use depends on the specific medical condition being investigated and the patient’s individual needs.
Scanning process:
An ultrasound involves the patient lying down and having a gel applied onto the target area. The trained technician (sonographer) will then run a small device called a transducer (probe) across it, pressing gently but firmly.
An MRI has the patient rolled into a large and cylindrical tube (which is the MRI scanner) and told to stay as still as possible for the whole duration (which can last for almost an hour).
Preparation:
An ultrasound requires a full bladder before the test to improve the clarity of the image, so the clinic will typically offer water and a waiting room until it is sufficiently full.
An MRI does not require any preparation like fasting or a full bladder, but it is essential that there are no metallic or magnetic items on or in you. So, items like jewelry must be removed.
Safety:
An ultrasound is completely safe and should not have any side effects.
An MRI scan itself is safe and should not have any side effects, but for certain cases they may ask to inject certain chemicals into the patient that can improve the quality of the image. The chemical is typically harmless and temporary but can have mild side effects like dizziness or getting a rash.
Things to note:
The process and nature of an MRI makes it unsuitable for some. To start with, people with metal implants or pacemakers are almost always ineligible for MRI scans since the MRI scan uses magnets. Furthermore, it is quite uncomfortable being inside the machine since the hole is narrow, so patients tend to feel anxiety or claustrophobic. This effect is exemplified from the loud sounds of the machine as it runs. An MRI also requires the person to stay as still as possible throughout to make sure the image is not blurry, meaning restless people like children may not be suited either.
Scanning capabilities:
A strength of an ultrasound is that it creates live pictures of the internal organs and is not confined to a single part. This means it can be utilized effectively and quickly to scan various parts while still in detail. However, ultrasounds are limited to only soft tissues like muscles and blood vessels and struggles to penetrate hard tissues like bones.
A strength of an MRI is that they are known to be extremely detailed, which is why MRIs are often preferred in diagnosing or examining in a medical setting. Unlike an ultrasound, MRIs can get images of hard tissues (the bones) much clearer, meaning MRIs are more suited for checking for things like bone or joint damage and areas covered with bones (like the brain). Additionally, MRIs are more suited for getting images large areas since an ultrasound’s vision is quite narrow (but makes up for it with its mobility).
Price:
Ultrasounds are relatively expensive but not egregiously so, depending on the place. Ultrasound scanning is widely available in places like private clinics or ultrasound centers, so ultrasounds are not exclusive to hospitals only. This means that some places like Blessono can offer reasonable prices considering factors like the equipment, maintenance, staff, and consultation.
MRIs are extremely expensive and almost always exclusive to large hospitals. This means the waiting time tends to be long but also that it is more expensive due to high demand. The extreme cost is understandable since the equipment itself is extremely expensive, along with needing specialized staff for various parts like running the machine and interpreting the imaging. Regardless, the daunting price makes people wary or hesitant on having and MRI.
Check out our Ultrasound & Health Screening Packages