What is a liver and gallbladder
The liver is the organ in the upper right side of the abdomen that plays a large role in the body’s metabolism and detoxification. It creates bile that helps emulsify fat (makes it easier to digest), stores or releases glycogen (as chemical that can be broken down to release energy later on) and also helps filter toxic or unwanted substances like alcohol and old red blood cells out of the blood into less harmful substances or out the body.
The gallbladder is the small organ that stores and releases the bile created by the liver.
Ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder
An ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder will look for structural information and abnormalities of them. This includes the size, shape, polyps (small mass of tissue) or lesions (damage). It’s also used to look for diseases like gallstones, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease.
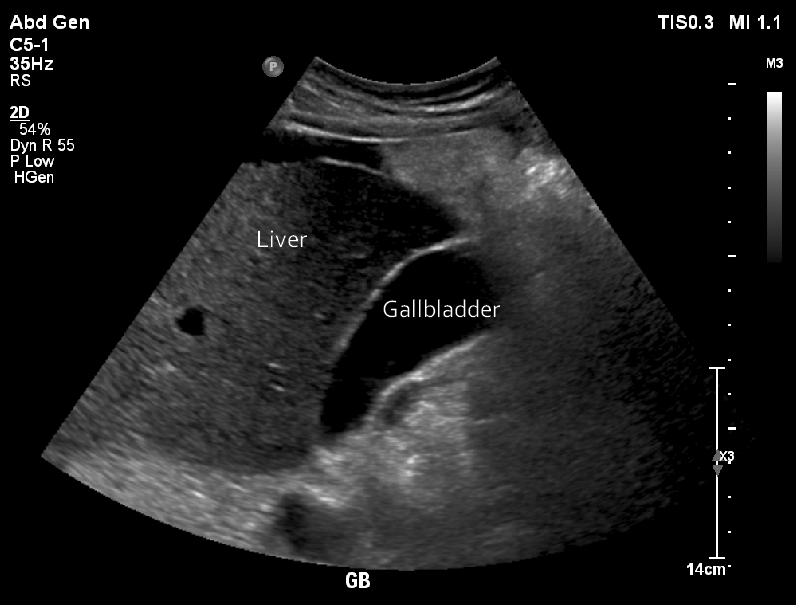
The gall bladder will appear black since it’s full of liquid (bile), which don’t reflect soundwaves as much as tissues/organs do. The liver is the large dark grey shape right next to the gall bladder. This can be seen from the ultrasound image.
Common problems – Fatty liver disease
Fatty liver and cirrhosis are quite serious diseases that can cause things like liver failure. You can read more about fatty liver and how it leads to cirrhosis on the Blessono blog
Common problems – Gallstones
Bile is typically a greenish-yellow liquid that is stored in the bile; however, it may harden and solidify and become “gallstones”. Gallstone formation is typically attributed to an unbalanced combination of substances in the bile (e.g too much/little cholesterol, bile salts etc.), which may come from your diet or genetics. They also can be tiny or big (ranging from a grain of sand to a golf ball) and may just pass through your body on their own. But once it blocks the bile duct (the tube that connects the liver, gall bladder, and small intestine), it’ll cause pain and put you in danger, meaning you’ll need treatment immediately.
Sometimes, gallstones can have no symptoms and may not cause harm. However, if the gallstone gets stuck in the bile duct, it can cause symptoms like:
- Sudden and increasing pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen or center of your abdomen
- Nausea or vomitting
It may be hard to determine if you have gallstones, or if the symptoms you’re feeling are from the gallstones. Fortunately, ultrasounds are quite effective at imaging gallstones for their sizes and location, allowing for early treatment like medication or surgery.