What are the carotid arteries:
The carotid arteries are the two arteries located at the sides of your neck which branches out into smaller divisions. The smaller division provides a blood supply to your face and neck, and another for the brain.
Ultrasound of the carotid artery:
The sonographer will place the ultrasound on your neck and press around, so you may be asked to reposition yourself so that you’re comfortable and your neck is more exposed. The sonographer will then examine the carotid artery and its branches, including things like the size and shape, along with checking for abnormalities like plaque on the walls.
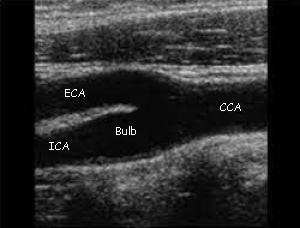
On the screen, you may see a large dark tube that branches off into two. It’s dark since it’s always full of liquid (blood), which ultrasounds pick up as black. The singular tube is known as the Common Carotid Artery (CCA), and it branches off into 2 divisions: Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) and External Carotid Artery (ECA). The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain, while the external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. You may also notice that on the ICA, the shape is slightly bulging. This part is called the carotid bulb/carotid sinus.
Your sonographer may look at each part one at a time rather than a whole for a more accurate measurement, so you may not see it all at once. You can try requesting your sonographer to get a full view if you want to see it.
Common problems – carotid artery disease
Carotid artery disease is when your carotid arteries get clogged by fatty deposits (plaques), thus making the blood vessel narrower or clogged. Carotid artery disease can seriously increase the chances of a stroke since the carotid artery gives blood to your brain. So, if the carotid artery supplies less blood to the brain due to a blockage or being too narrow, then the brain won’t receive enough blood or supplies in the blood (e.g oxygen), thus resulting in a stroke.
You may have no symptoms of a carotid artery disease/plaque building up in the carotid arteries until it’s too late. When it’s too late, then you may have a transient ischemic attack, a type of stroke where blood supply to a part of your brain is briefly blocked. These symptoms include:
- Numbness or weakness in face or limbs
- Blurred vision or temporary blindness
- Slurred speech
- Paralysis or loss of coordination
A stroke is an extremely serious condition that results in a lot of death, with strokes/cerebrovascular diseases being Malaysia’s third leading cause of death. Although a stroke can’t be detected with an ultrasound, the carotid arteries are able to be scanned before having a stroke. Early detection of narrowed blood vessels will become vital information for your doctors if you do arrive at the hospital with a stroke. It will also allow early treatment to unclog your arteries to reduce the chances of having a stroke.